
Figure 1: Displays a picture of a working bottle rocket.
A bottle rocket, or more commonly water rocket, is a type of model rocket using water as its reaction mass.
The water is forced out by a pressurized gas, typically compressed air. Like all rocket engines, it operates on the principle of Newton's third law of motion .
Reference 1
Newton's third law is: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
The statement means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects.
The size of the forces on the first object equals the size of the force on the second object.
Reference 2
Rockets work by ejecting something out of the back and a so-called 'reaction force' then pushes the body of the rocket forward.
In bottle rockets, the energy to force the water out the bottom of the water is stored as air pressure inside the bottle.
The energy supplied to the rocket through the use of an air pump. The air pressure inside builds up and pushes on the water.
Reference 3
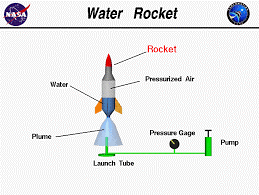
Figure 2: Displays a diagram of each compartment of a bottle or water rocket.